

The measurement of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) lactate has been shown to have utility in the rapid differentiation of bacterial meningitis from viral meningitis. This case illustrates the importance of broadening the differential when otherwise healthy patients present with nonspecific or common symptoms.Cryptococcal meningitis, cerebrospinal fluid, lactic acid, prognostic marker, mortality
Cryptococcal meningitis csf findings serial#
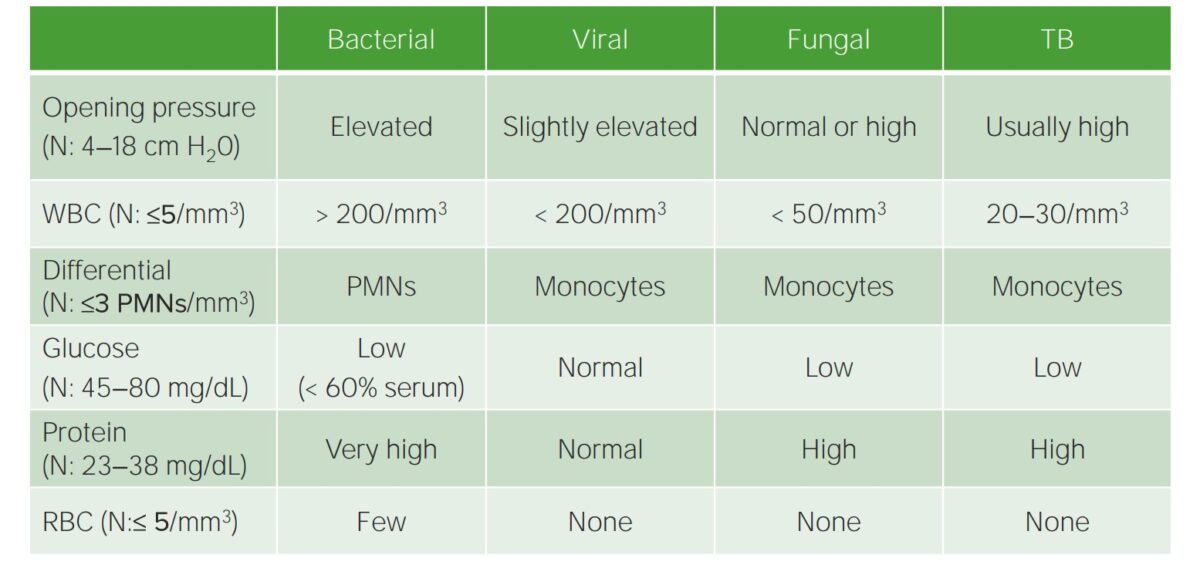
Management usually entails both antifungal therapy and intracranial pressure control, especially to reduce opening pressures <= 20cm H20, via serial lumbar punctures or VP shunt if refractory.Ĭonclusions: While Cryptococcal meningitis is commonly found in immunocompromised patients, it should also be considered in immunocompetent hosts with symptoms of altered mental status, gait instability, hydrocephalus, and lymphocytic predominance on CSF findings. Lymphocytic predominance with low glucose and elevated protein are also commonly found, while CSF culture is considered the gold standard in diagnosis. For lumbar punctures, most notably patients with cryptococcal meningitis show marked elevation of opening pressure, which was present in our patient (OP 23). In our case, the exact predisposing factor is unknown, but may be in part due to his alcoholic cirrhosis.As to radiographic imaging, head CT is frequently unremarkable though may demonstrate hydrocephalus. While HIV and malignancy are known causes of immunosuppression, other comorbidities, ie alcoholism, diabetes, cirrhosis, certain autoimmune diseases, may precipitate mild states of immunosuppression, predisposing hosts to opportunistic infections. Some evidence suggests isolates are of increased pathogenicity, while other papers postulate subtle defects in host immunity may lead to disease. Subsequent meningitis is thought to potentially result from inhalation of the organism with hematogenous spread into the central nervous system.For immunocompetent hosts, the pathophysiology is even less understood. While Cryptococcus neoformans is classically associated with bird dropping exposures, the relationship from exposure to disease is not well defined. Given signs of continued hydrocephalus, ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt was performed to improve drainage and indirectly, patient’s mentation.ĭiscussion: Cryptococcal meningitis in non-HIV patients is rare with only a few cases published on cryptococcal infection in immunocompetent hosts. As a result, patient was started on amphotericin and flucytosine for a two-week course, with later down-titration to fluconazole 400mg daily. Ultimately, cryptococcal antigen resulted positive (titers 1:20) on CSF fungal culture.

A lumbar puncture was performed from suspicion of normal pressure hydrocephalus given CT findings however, CSF fluid results were significant for low glucose, elevated protein, and lymphocytic predominance, which was most concerning for fungal or tuberculosis etiology. Patient was given thiamine and admitted for encephalopathy workup. A non-contrast head CT showed new increased size of lateral and third ventricles out of proportion to sulcal prominence, encephalomalacia from remote infarcts, and significant increase in nonspecific confluent deep white matter hypo-attenuation. Physical exam showed no focal neurological deficits, though notable for wide based gait. In ED, patient was oriented to name only, tachycardic otherwise afebrile and normotensive. Social history was pertinent for drinking multiple beers daily for years. Medical history was significant for alcoholic cirrhosis and prior (2018) cardioembolic strokes with no deficits. Case Presentation: A 51-year-old man was brought in by family for confusion and unsteady gait for a few days.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
